Die GYPT-Aufgaben sind offen gestellte Forschungsfragen, die anhand von Experimenten untersucht werden. Ziel ist es, das beschriebene Phänomen mit Hilfe von Versuchen, Simulationen und Theorien physikalisch zu beschreiben und zu erklären. Zu vielen Aufgaben gibt es dementsprechend keine korrekte oder vollständige Lösung.
Auf unserer Website finden sich grundlegende Hinweise zur Bearbeitung der Aufgaben sowie einige Ressourcen und Materialien, die deine Forschungsarbeit erleichtern. Außerdem wird jede Aufgabe von einem/einer Projektmentor:in betreut, der/die dir bei deinen Experimenten sowie der Aufbereitung der Ergebnisse für das Turnier beratend zur Seite steht.
Den Namen und eine Kontaktmöglichkeit zum/zur Mentor:in sowie weitere Unterstützungsangebote findest du jeweils in der linken Randspalte neben der Beschreibung der Aufgabe. Für alle anderen Fragen kannst du auch jederzeit die GYPT-Organisator:innen anschreiben.
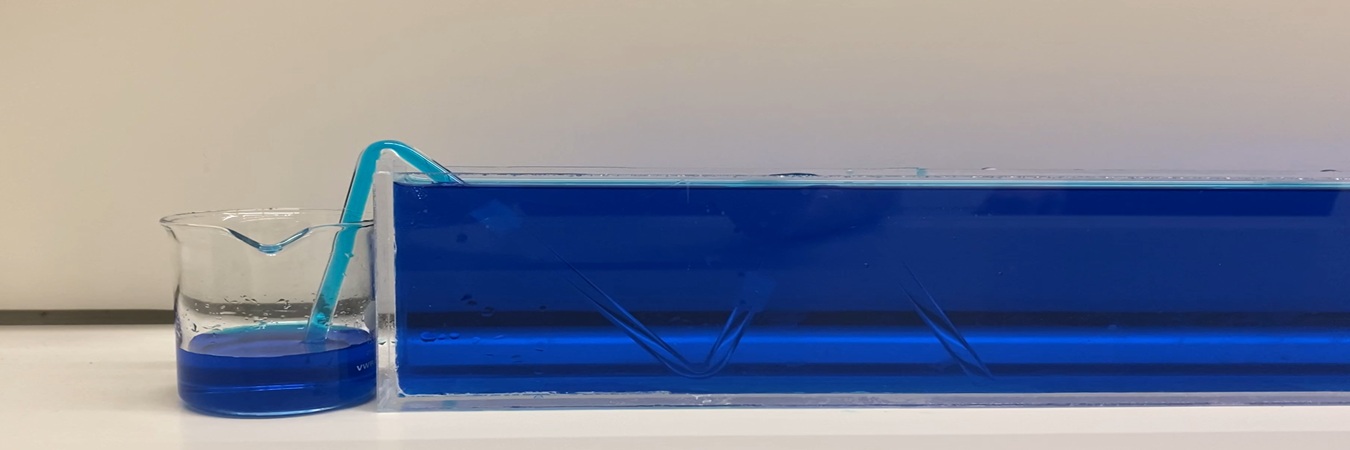

A self-starting siphon can be made using a piece of rigid tubing bent into a specific shape. When the siphon is partially immersed in water, it begins siphoning water without the need for initial suction. Investigate how the relevant parameters, such as the geometry, affect the siphoning process.
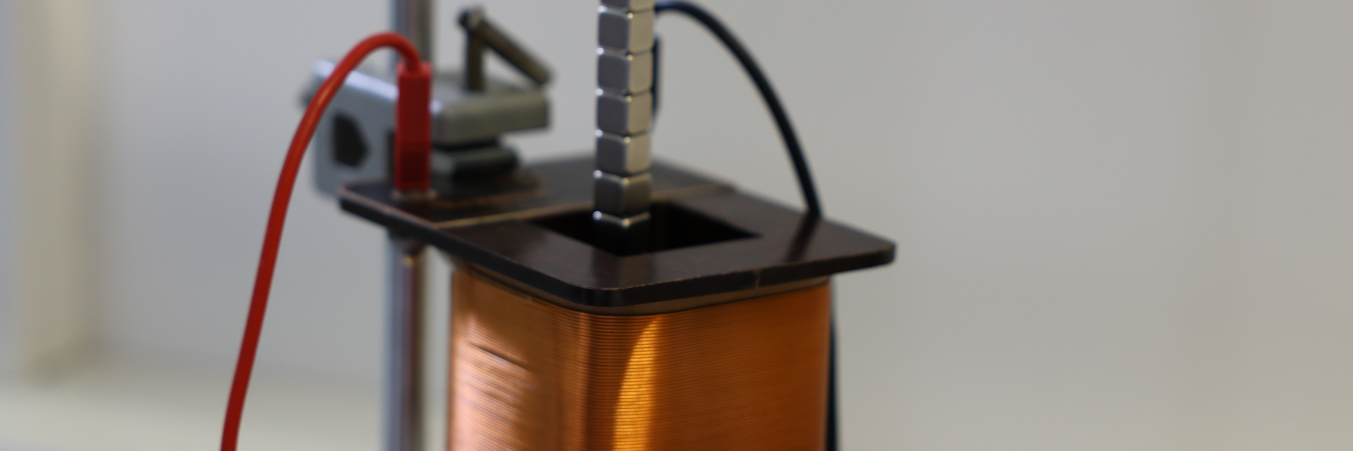

A magnet suspended by a spring will display simple harmonic motion when displaced. If the magnet oscillates within a coil connected to a resistor, its motion will be damped. Investigate the factors that affect the damping.
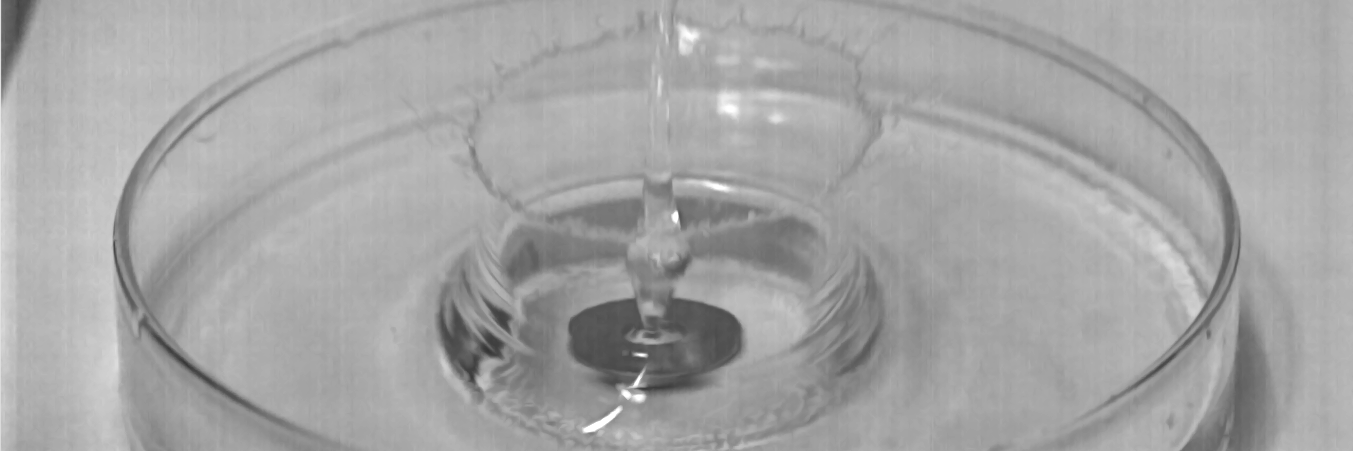

When a flat metal ring falls from a certain height into a water tank, it generates a fountain that can shoot water high into the air. How does the maximum height of the fountain depend on the ring's parameters?
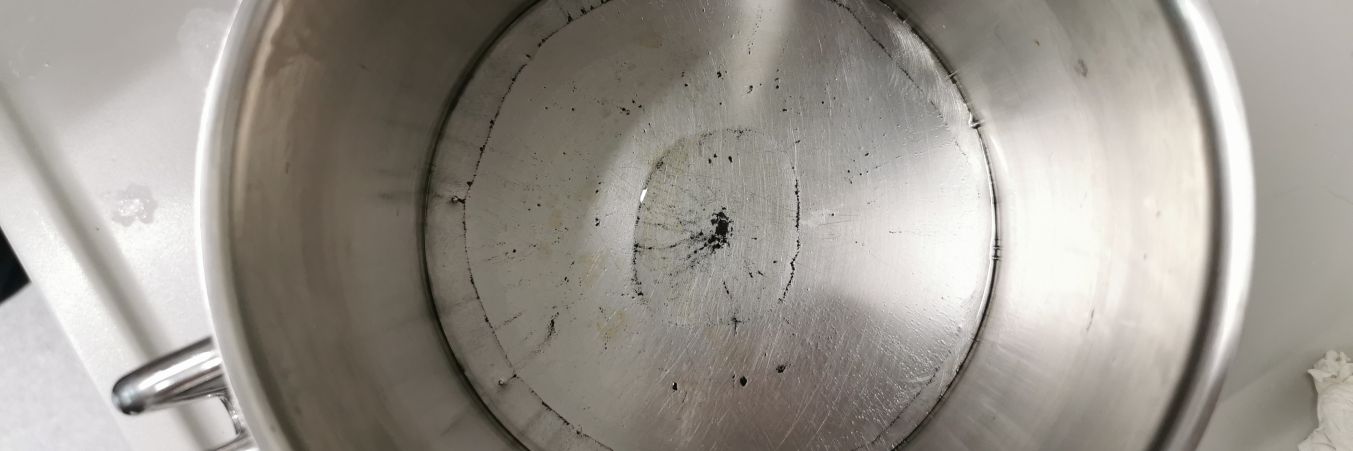

A thin layer of cooking oil on a flat metal surface flows outwards when heated. Investigate the phenomenon and its dependence on relevant parameters.
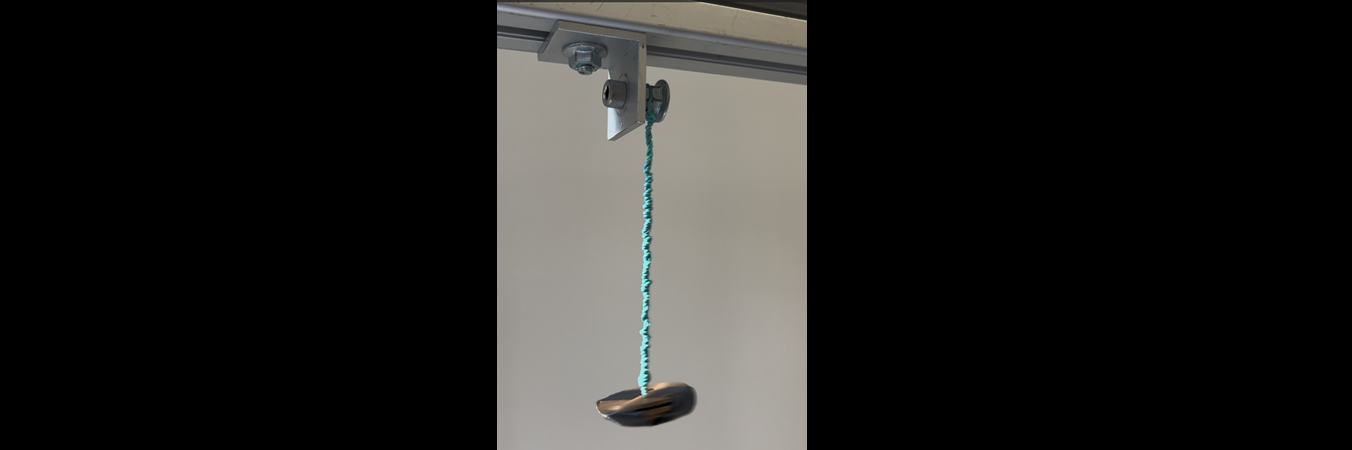

Suspend a metal ball from a fixed support using a rubber band and twist it many times around its vertical axis. When the ball is released, standing waves are formed on the rubber band. Investigate this phenomenon and study how the wave depends on relevant parameters.
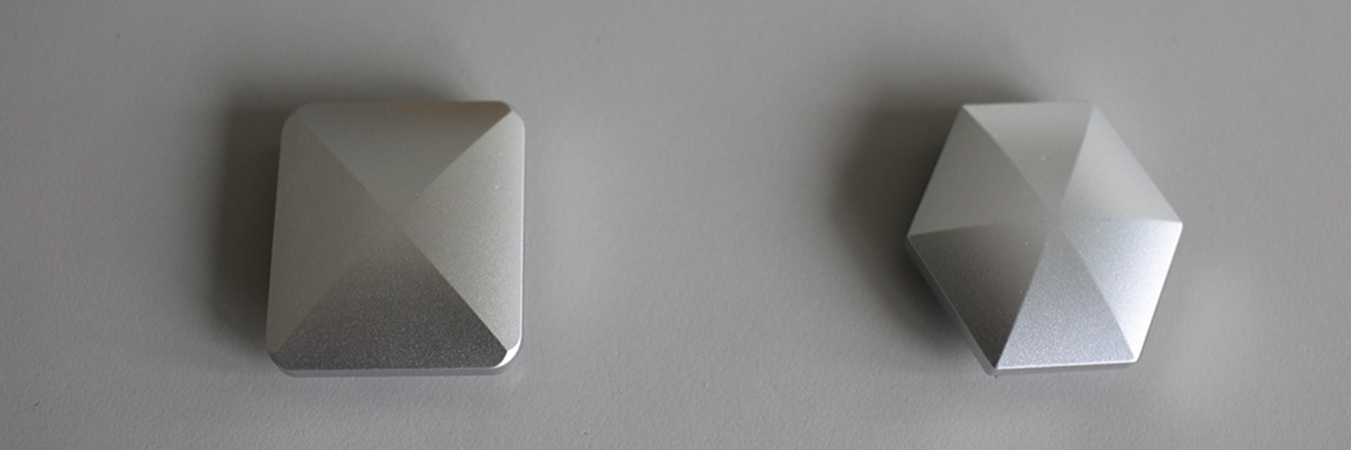

A Flipo Flip toy can roll for multiple turns even though its shape is not circular. Investigate how its motion depends on parameters such as geometry and the initial release conditions.
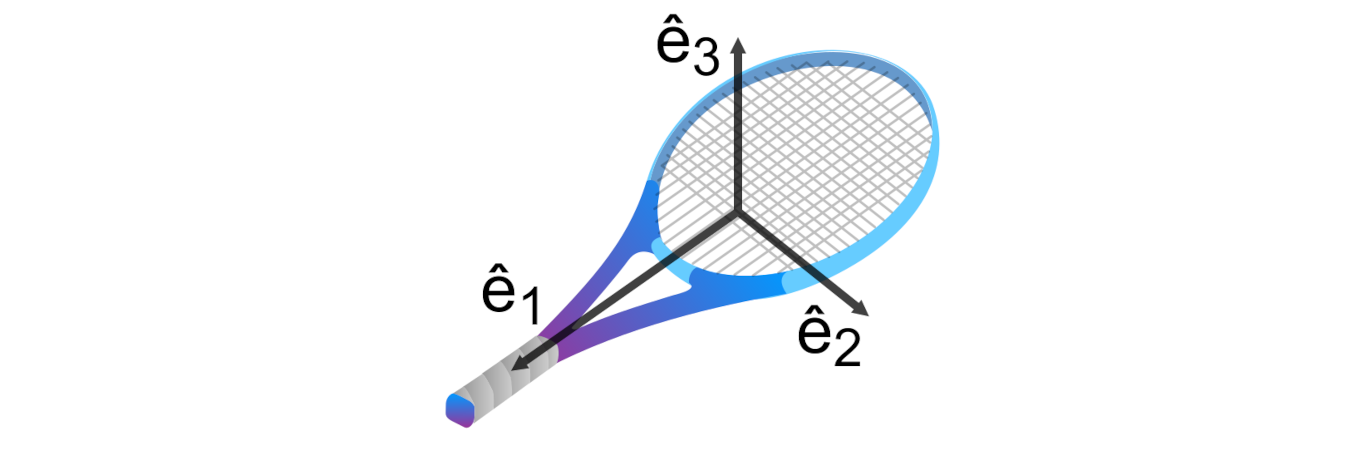
When an object with different principal moments of inertia about each axis is thrown while it rotates, it can suddenly start rotating around an axis different from the one it was initially rotating about. Investigate how the rotational motion of such an object is affected by relevant parameters during its free fall.
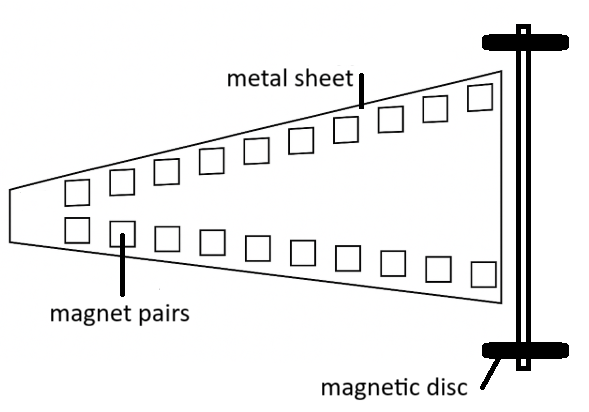
Fix magnets in pairs onto a metal sheet as shown. If you attach two magnetic discs onto an axle this "vehicle" will accelerate over the rows of magnets under certain conditions. Investigate the phenomenon.
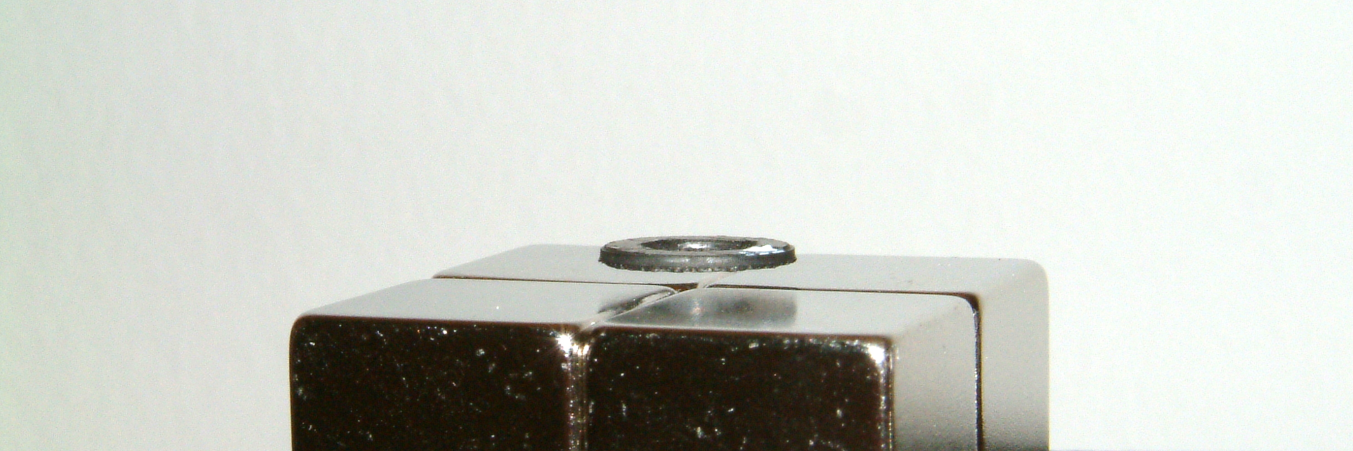

When arranged in a specific configuration, small graphite sheets can levitate on neodymium magnets. By shining light onto the surface of the graphite sheet, it is possible to control its movement. Explain and investigate the phenomenon.
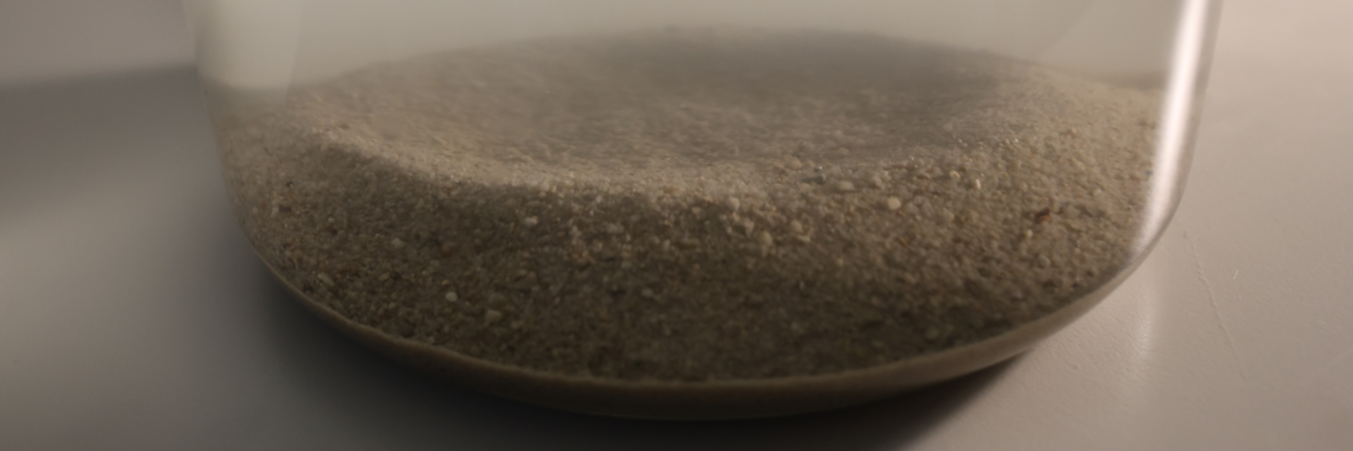

If you release sand or similar granular material in a container filled with water, the material will sink to the bottom and may form a crater-like structure. Explain and investigate the phenomenon.
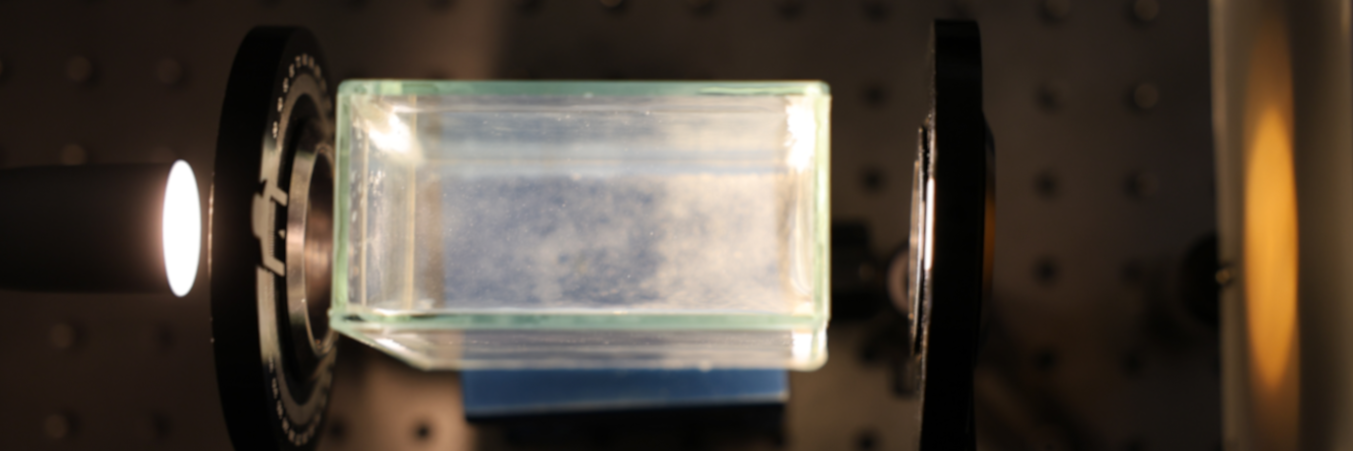
Pass linearly polarised white light through a column of sugar solution. When transmitted light is observed through a polariser it may appear coloured. Rotate the polariser, and the transmitted light colour may change. Construct such a sweet monochromator and optimise for the narrowest light wavelength bandwidth.
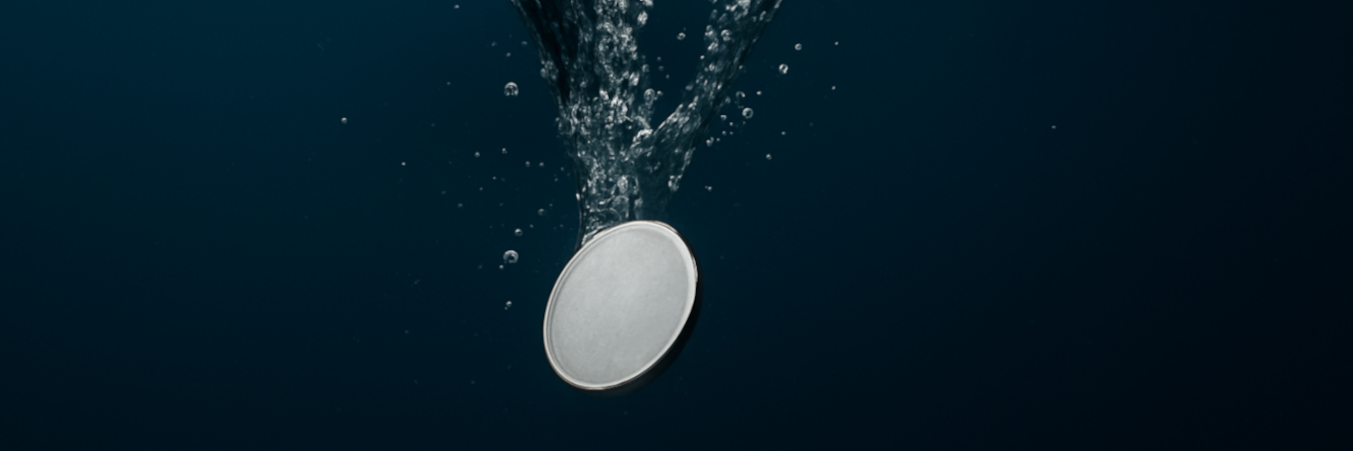

The motion of a coin falling to the bottom of a tank filled with liquid can be remarkably similar to the fluttering and tumbling of a falling autumn leaf. Investigate how the motion of the coin depends on relevant parameters.
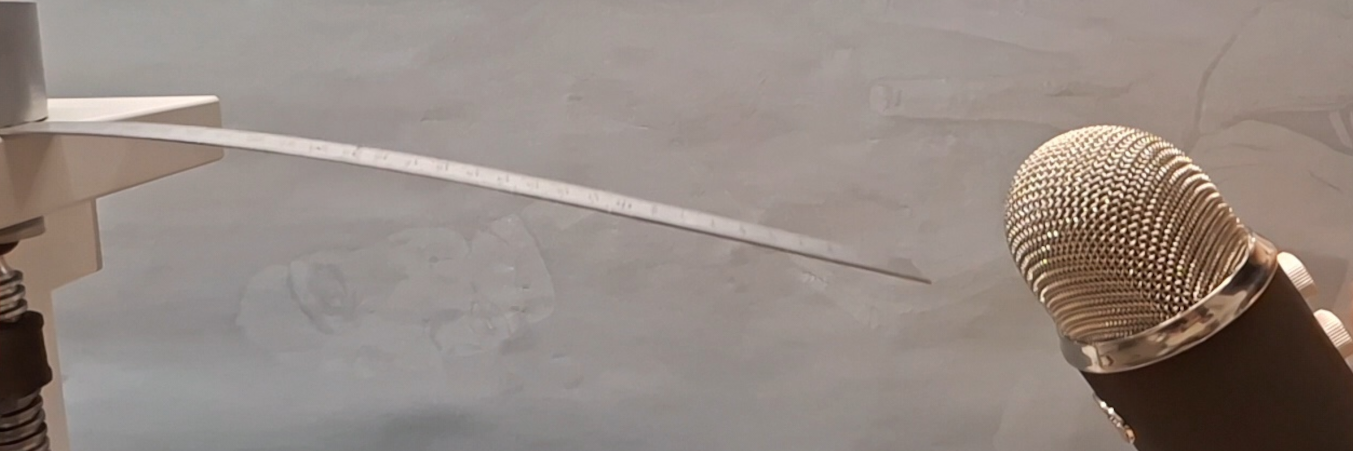

When a ruler is clamped at one end and struck, it oscillates and emits a characteristic sound. Investigate how the sound depends on relevant parameters.
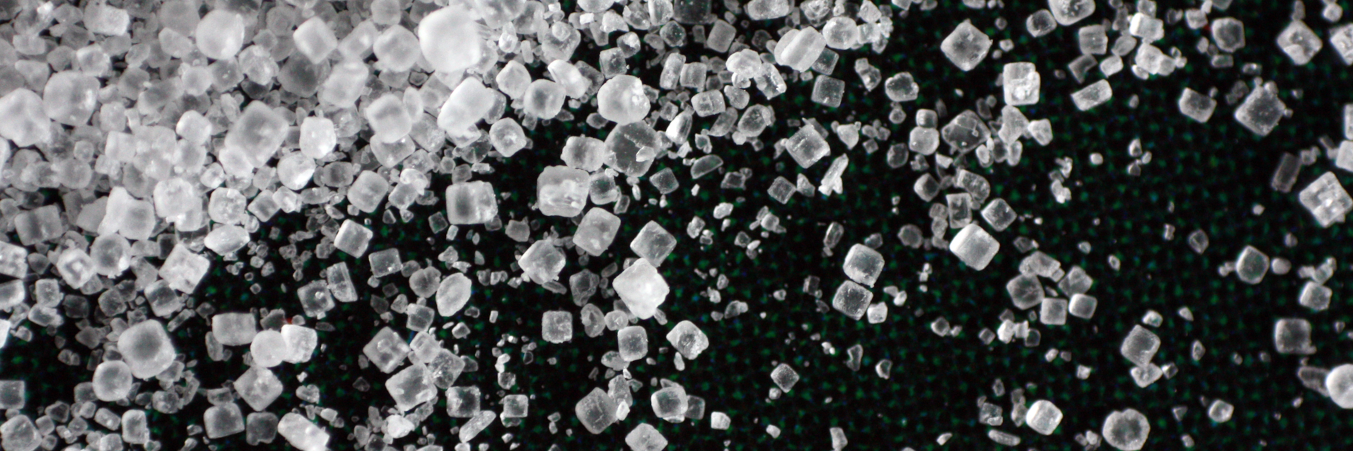

Observe the evaporation of a drop of table salt solution on a warm hydrophobic surface. After the water evaporates, a variety of characteristic crystal shapes remain. Research and explain this phenomenon.
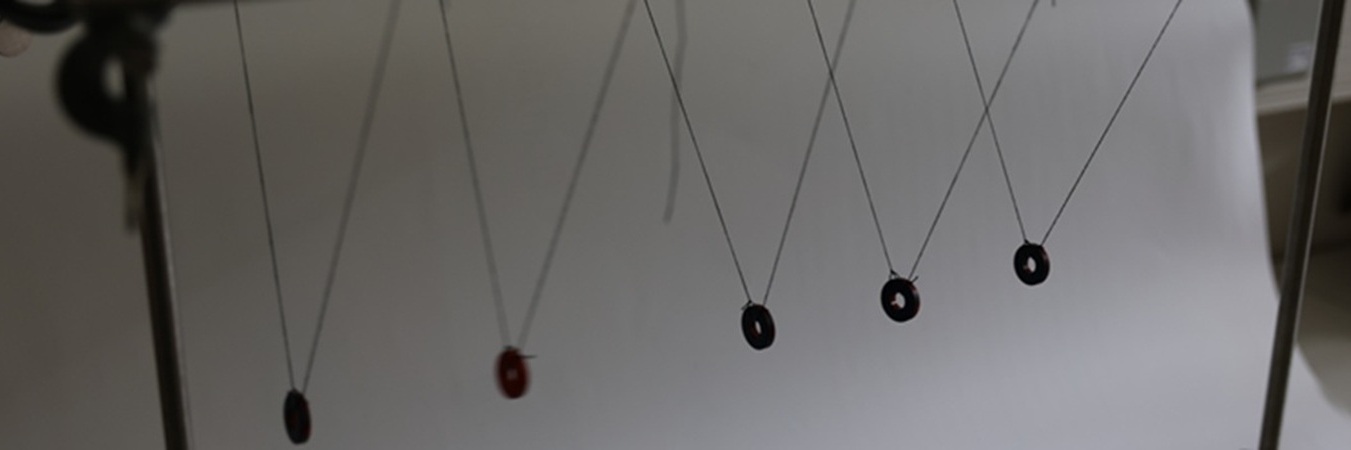

Repulsing, non-touching magnets are used instead of colliding balls to make a new type of Newton's cradle. The new cradle can act in a similar way to a regular cradle, but can also exhibit other interesting behaviour. Explain and study the movement of this magnetic cradle.
Aufgaben vorheriger Jahre im Archiv